Good news, if it can be said, for my fellow Malagasy citizens: Since 6th of December 2014, Google Translate has been allowing them to see almost any web page in their mother tongue in addition to 89 others. Many people, myself included, have been waiting for this moment that would have come sooner or later. First of all, I would like to address a big thanks to all people that have made this possible. Thanks to you, the Malagasy language is getting further integrated into the polyglot Web world. You’ve also given a chance to the 15 million monolinguals to have an approximate understanding of what other people have written using other languages are writing.
Before Google Translate
Before we’ve got Google translate to translate almost anything in our language, including curse words, several websites have helped us Malagasy and other language enthusiasts to write corpora in a proper way in our mother tongue: many of us have already heard about Freelang, tenymalagasy.org and so on. The only drawback of these website is that they do not work in a collaborative way: they are not «crowdsourced». Wikibolana is a Malagasy language crowdsourced dictionary, but I have been so far the one that has generated most of its content.
Is it really that good?
Well, let’s be honest: absolute accuracy has been the motto for no machine translation system ever. But for a brand new language on Google Translate, Malagasy is… quite good. Daring to translate a language with such an unusual syntax like Malagasy is already a huge challenge, a challenge worth to be accepted. At first sight, idiomatic sentences and expressions are fairly well handled. Still when it comes to very complex sentences, it is a mess: verbs are at the wrong place, which either gives the sentence a completely different meaning, or makes it look like an incomplete sentence. There are also some fails as the one in the screen shot below.
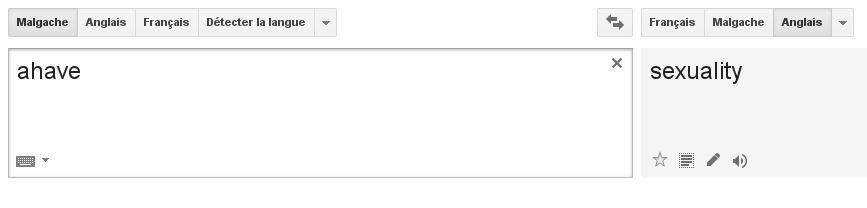
Let’s see an example of a translation of a paragraph of the article Madagascar in the English Wikipedia:
Original in English In 2012, the population of Madagascar was estimated at just over 22 million, 90 percent of whom live on less than two dollars per day. Malagasy and French are both official languages of the state. […] The island’s elephant birds, a family of endemic giant ratites, went extinct in 17th century or earlier, most probably due to human hunting of adult birds and poaching of their large eggs for food. Google-translated in Malagasy (as of December 2014) Tamin’ny 2012, ny mponina ao Madagasikara dia tombanana ho 22 tapitrisa mahery kely, 90 isan-jaton’ny izay [no] miaina amin’ny [vola] latsaky ny roa dolara isan’andro. Malagasy sy Frantsay dia samy fiteny ofisialy ao amin’ny fanjakana. […] Ny nosy vorona ny elefanta, ny fianakaviana ny fizahantany ratites goavana, dia efa lany tamingana tamin’ny taonjato faha-17, na teo aloha, indrindra noho ny olona angamba ny olon-dehibe ny fihazana sy ny vorona lehibe Fihazana ny atodiny ho sakafo.
The green-coloured sentences are syntactically correct without correction. The first one has required the red words in square brackets to sound correct. The third one hurt my brain: “The elephants are a bird island, the family of big tourists, have gone extinct in 17th century, or before, perhaps because of people, adults, hunting and adult birds who have their eggs hunted for food.” It hurt to understand, and also hurt to back-translate. Astonishingly making a round-trip translation has given a correct sentence in English, so please always have your translations checked human translators.
Efforts to be continued
One can take part to increase translation accuracy by translating articles by using the Google translator toolkit, or by using and correcting translations provided by Google translate itself.
Leave a Reply